Connections Pane
The Connections Pane allows you to explore database connections created within your R or Python sessions. It also includes basic support for storing and managing connection strings for future usage.
Opening a connection using R
To open a connection in Positron Connections Pane, you need to connect to a database using any package that supports the connections contract, such as odbc, sparklyr, bigrquery, and others.
The Positron Connections Pane implements RStudio’s connections contract; this means that any package that works within RStudio’s Connections Pane should work within the Positron Connections Pane.
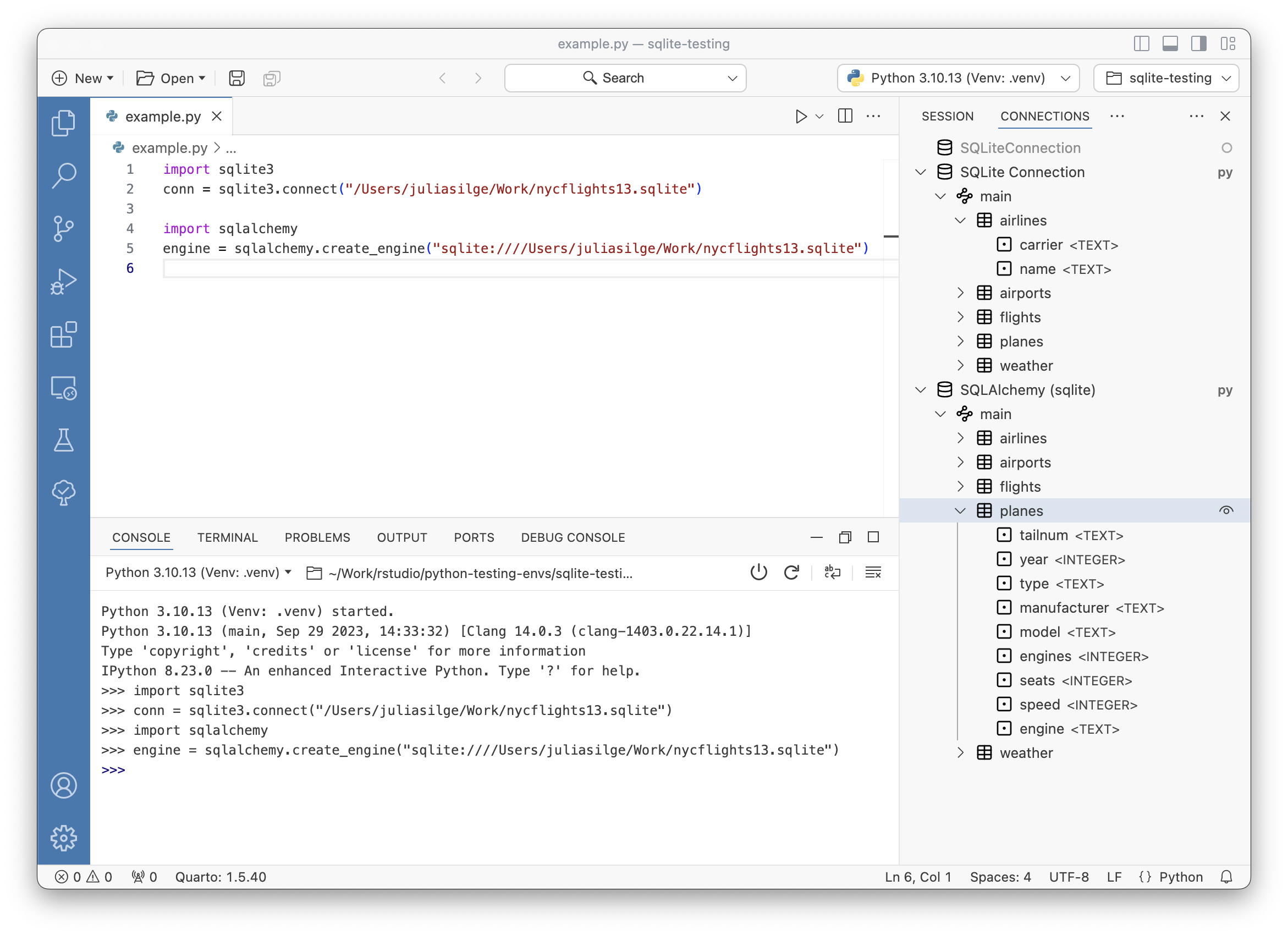
Here is an example of how to open a connection using the connections package to open a SQLite connection:
tmp <- tempfile()
dir.create(tmp)
dbplyr::nycflights13_sqlite(path = tmp)
con <- connections::connection_open(RSQLite::SQLite(), file.path(tmp, "nycflights13.sqlite"))You can also open an existing connection from the Variables Pane, as shown below for Python, and you can find more information about connecting to a specific database from Posit Solutions Engineering.
Opening a connection using Python
Currently we support connections created using the sqlite3 and SQLAlchemy modules. To open a connection in the Connections Pane, create a top level object that represents the connection/engine.
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect("nycflights13.sqlite")You can then either use %connection_show conn to open the connection in the Connections Pane or click on the database icon that appears close to the object name in the Variables Pane.
That will bring up the Connections Pane, allowing you to navigate the database.
Extending the Connections Pane
The Connections Pane can be extended by:
- Adding support for browsing and managing a new connection type in the Connections Pane.
- Extending the “New connections” modal to support creating a connection of a new type.
Adding new connection types
Currently connection types are extensible in R using the RStudio connections contract. Refer to the RStudio connections contract documentation for more information on how to implement a new connection type.
For Python, we don’t currently support an external extension mechanism. The Connections Pane can be extended by implementing a subclass of the Connection class defined in connections.py and submitting a PR to the Positron repository. Refer to SQLite3Connection for an example.
Extending the “New connections” modal
The “New connections” modal allows users to easily create connections to different databases. It helps users create a connection by providing a form to fill in the connection details.
The modal can be extended by creating an extension for Positron; see Extension Development for more information.
In order for an extension to provide support for a new connection type, it needs to implement and register a positron.ConnectionsDriver. A driver provides metadata about the connection type and implements callbacks that are used to install dependencies required to create the connection, connect with the database, and disconnect.
The definition can be found in positron.d.ts; look for ConnectionsDriver.
export interface ConnectionsDriver {
/**
* The unique identifier for the driver.
*/
driverId: string;
/**
* The metadata for the driver.
*/
metadata: ConnectionsDriverMetadata;
/**
* Generates the connection code based on the inputs.
*/
generateCode?: (inputs: Array<ConnectionsInput>) => string;
/**
* Connect session.
*/
connect?: (code: string) => Promise<void>;
/**
* Checks if the dependencies for the driver are installed
* and functioning.
*/
checkDependencies?: () => Promise<boolean>;
/**
* Installs the dependencies for the driver.
* For instance, R packages would install the required
* R packages, and or other dependencies.
*/
installDependencies?: () => Promise<boolean>;
}To register a driver, extensions need to call positron.connections.registerConnectionDriver() with the driver instance as an argument.
Refer to drivers.ts for examples of drivers implemented in the Positron Connections extension.